Most Important Biology Diagram For NEET UG 2026: Diagrams play a decisive role in NEET UG Biology, as a significant number of questions are either directly based on diagrams or become easier when concepts are visualized clearly. To strengthen daily revision and boost diagram-based accuracy, we have decided to publish 3 important NEET UG Biology diagrams every day as part of a focused revision series.
These carefully selected diagrams are frequently asked in the exam and are designed to help aspirants revise faster, retain concepts longer, and avoid common labeling mistakes. Regular practice of these high-yield diagrams will sharpen visual memory and play a crucial role in pushing your Biology score and overall NEET UG rank.
1. DNA Double Helix
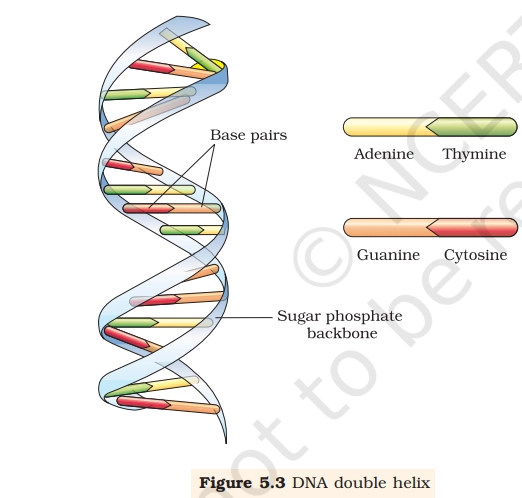
The DNA Double Helix model was proposed by Watson and Crick (1953) based on X-ray diffraction data by Rosalind Franklin. This structure explains replication, transcription, heredity, and genetic continuity, making it a core NEET UG topic.
Points to Remember:
- DNA consists of two polynucleotide strands
- Strands are antiparallel (5′ → 3′ & 3′ → 5′)
- Backbone is made of alternating sugar and phosphate
- Bases are attached to sugar via N-glycosidic bond
- Base pairing rule:
- A = T (2 H-bonds)
- G ≡ C (3 H-bonds)
- Helix is right-handed
- One turn = 10 base pairs
- Pitch of helix = 3.4 nm
- Distance between two base pairs = 0.34 nm
NEET Memory Tips:
- “AT = 2, GC = 3” → Hydrogen bonds
- “Pure DNA is Right-handed”
- Antiparallel = Opposite direction strands
- Sugar-Phosphate = Outside & Bases = Inside
Practice MCQs From the Diagram
Q.1. The hydrogen bond present between Adenine and Thymine is:
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
Q.2. Which component forms the backbone of DNA?
A. Nitrogenous bases
B. Hydrogen bonds
C. Sugar and phosphate
D. Ribose sugar
Q.3. DNA strands are said to be antiparallel because:
A. Bases face opposite directions
B. Sugar-phosphate chains run in opposite directions
C. Hydrogen bonds are opposite
D. Helix turns in opposite direction
Q.4. Which base pair has three hydrogen bonds?
A. A-T
B. A-G
C. G-C
D. T-C
Q.5. Distance between two consecutive base pairs in DNA is:
A. 0.34 nm
B. 3.4 nm
C. 10 nm
D. 34 nm
Answers:
Ans.1. B
Ans.2. C
Ans.3. B
Ans.4. C
Ans.5. A
2. Structure of Bacteriophage
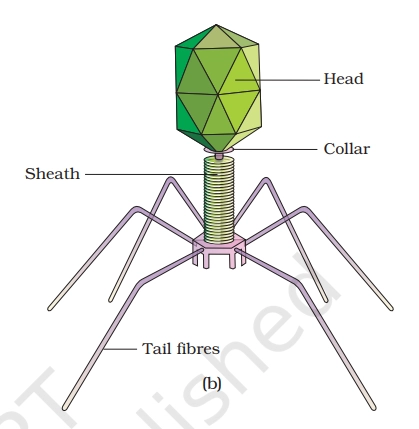
A bacteriophage is a virus that infects a bacterium. Bacteriophages were first discovered in 1915 by William Twort, and in 1917 by Felix d’Herelle realized that they had the potential to kill bacteria.
Points to Remember:
| Part | Description |
|---|---|
| Head (Capsid) | Protein coat, icosahedral in shape |
| Genetic Material | Double-stranded DNA |
| Collar | Connects head to tail |
| Tail Tube & Sheath | Hollow tube for injecting DNA |
| Base Plate (bottom ring above the tail fibers) | Helps in attachment to bacteria |
| Tail Fibers | Recognize and bind to host cell |
NEET Memory Tips:
- Bacteriophage = Virus that infects bacteria
- Shape looks like space shuttle / lunar lander
- DNA virus (not RNA)
- Tail fibers = attachment
- Tail tube = injection
Read Also: NCERT Diagrams for NEET UG 2026: The Most Underrated NEET Scoring Tool
Practice MCQs from Structure of Bacteriophage
Q1. The genetic material present in a bacteriophage is:
A. ssRNA
B. dsRNA
C. dsDNA
D. ssDNA
Q2. Which part of bacteriophage helps in attachment to the host?
A. Head
B. Collar
C. Tail fibers
D. Capsomere
Q3. Shape of bacteriophage head is:
A. Helical
B. Cuboidal
C. Icosahedral
D. Spherical
Q4. Bacteriophage infects:
A. Plants
B. Animals
C. Bacteria
D. Fungi
Answers:
Ans.1. C.
Ans.2. C.
Ans.3. C.
Ans.4. C.
3. Structure Of Nephron
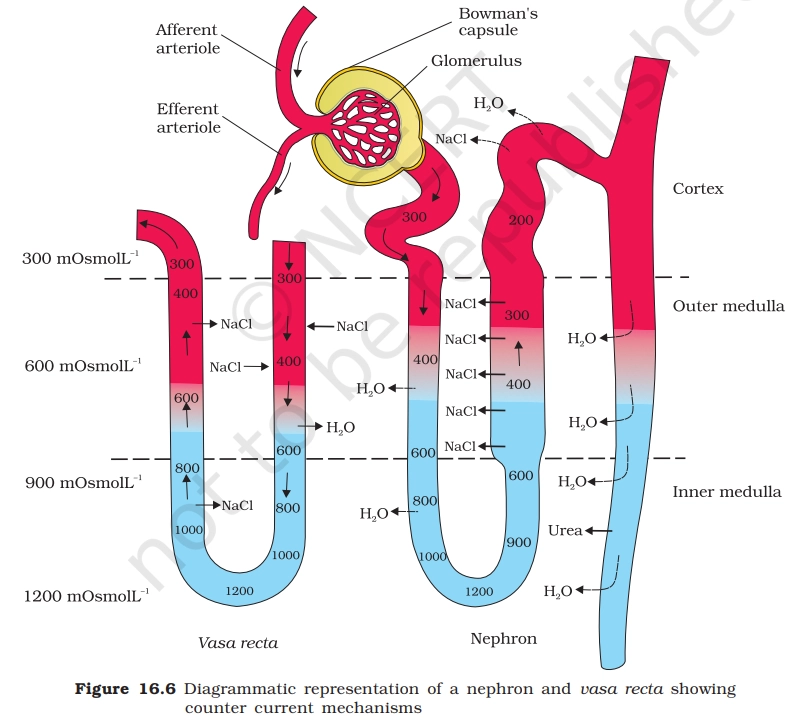
The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each human kidney contains about 1-1.5 million nephrons, and each nephron is specially designed to filter blood and form urine.
Points to Remember
| Part | Function |
|---|---|
| Glomerulus | Ultrafiltration of blood |
| Bowman’s Capsule | Collects filtrate |
| PCT | Maximum reabsorption |
| Loop of Henle | Concentrates urine |
| DCT | Selective secretion |
| Collecting Duct | Final urine formation |
Memory Tips:
- PCT = maximum reabsorption (65-70%)
- Glomerulus = filtration only
- Loop of Henle = water & NaCl balance
- Blood flow:
- Afferent arteriole → Glomerulus → Efferent arteriole
MCQs from Nephron Diagram
Q1. The process of ultrafiltration occurs in:
A. PCT
B. DCT
C. Loop of Henle
D. Glomerulus
Q2. Maximum reabsorption of glucose occurs in:
A. DCT
B. Loop of Henle
C. PCT
D. Collecting duct
Q3. Which part of nephron helps in concentration of urine?
A. Bowman’s capsule
B. Loop of Henle
C. PCT
D. Glomerulus
Q4. The filtrate formed in Bowman’s capsule is similar to:
A. Blood
B. Plasma with proteins
C. Plasma without proteins
D. Urine
Answers:
Ans.1. D
Ans.2. C
Ans.3. B
Ans.4. C
An accurate understanding of NCERT diagrams helps in quick identification, eliminates confusion in options, and reduces silly mistakes. Many NEET toppers attribute their high Biology scores to consistent diagram practice, as it strengthens conceptual clarity and improves recall under exam pressure. Mastering important diagrams is not optional: it is a high-scoring strategy for aspirants aiming for 650+ marks in NEET UG.
All The Best!
Let us know in the comments if you’d like us to share daily diagram revision posts.
Read Also: What NEET UG 2026 Aspirants Must Learn From Last Year’s Paper Analysis

