Most Important Biology Diagram For NEET UG 2026: Day 6 of the Most Important NEET Diagrams series is here to prove that a single well-understood diagram can save you from multiple tricky MCQs in the exam hall. From smart labelling tricks to quick memory hacks, today’s focus will help you turn confusing lines and arrows into crystal-clear concepts, because in NEET, the right diagram at the right time can be your secret shortcut to a higher score.
Female Reproductive System
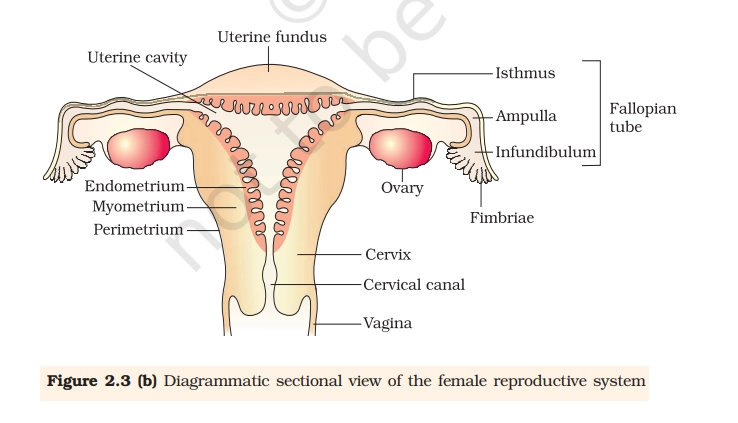
The female reproductive system includes internal organs like the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina, plus external structures such as the vulva and mammary glands. These enable gamete production, fertilization, pregnancy, and hormone regulation.
Key Points To Remember
- Ovaries: Paired gonads producing ova (eggs) and hormones estrogen/progesterone; located in the pelvic cavity.
- Fallopian tubes (oviducts): Transport eggs from ovaries to uterus; site of fertilization (10-12 cm long).
- Infundibulum: Funnel-shaped end of the fallopian tube near the ovary, featuring fimbriae.
- Ampulla: Widest expanded portion of the fallopian tube where fertilization typically occurs.
- Fimbriae: Finger-like projections at the infundibulum that sweep the ovum from the ovary into the tube.
- Uterus: Inverted pear-shaped muscular organ for embryo implantation and development.
- Uterine cavity: Central hollow space within the uterus where the embryo implants and develops.
- Uterine fundus: Dome-shaped upper part of the uterus above the entry of the fallopian tubes.
- Endometrium: Inner mucosal layer of the uterus that thickens during the menstrual cycle and sheds if no pregnancy occurs.
- Myometrium: Thick middle muscular layer of the uterus responsible for contractions during labor.
- Perimetrium: Thin outer serous layer covering the uterus.
- Cervix: Lower uterus part connecting to vagina; produces mucus.
- Isthmus: Narrow lower segment of the uterus between the fundus and cervix.
- Vagina: Muscular canal for intercourse, menstruation, and childbirth.
- Vulva: Includes labia majora/minora (protection), clitoris (arousal), mons pubis, and Bartholin’s glands (lubrication).
Practice Questions
Q.1. In a normal human female, which structure is the primary site of fertilization?
A. Vagina
B. Ampullary–isthmic junction of the oviduct
C. Uterus
D. Cervix
Q.2. Which hormone is primarily responsible for the proliferation of the endometrium during the menstrual cycle?
A. Estrogen
B. Prolactin
C. Progesterone
D. Oxytocin
Q.3. In a typical 28-day menstrual cycle, ovulation most likely occurs around which day, counting from the first day of menstruation?
A. Day 21
B. Day 28
C. Day 7
D. Day 14
Q.4. Which of the following correctly describes the role of the corpus luteum in the female reproductive cycle?
A. It is the site of oogenesis throughout life
B. It stores mature sperm until fertilization
C. It secretes progesterone and estrogen to maintain the endometrium
D. It produces large amounts of follicle-stimulating hormone throughout pregnancy
Q.5. Which combination of structures is correctly matched with its primary function in the female reproductive system?
A. Fimbriae – site of implantation
B. Ovary – storage of developing embryo
C. Endometrium – production of oocytes
D. Cervix – passage for sperm into uterus
Mammary Gland
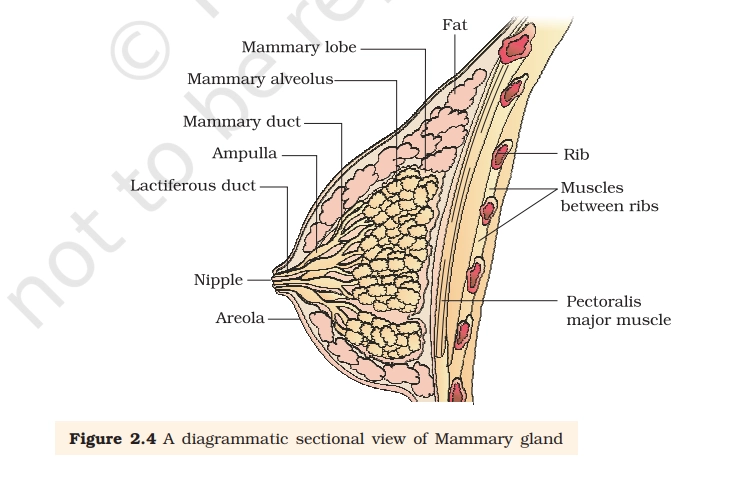
Mammary gland is a specialized, milk-secreting accessory gland of the female reproductive system, located in the pectoral region of the breasts. Derived from modified apocrine sweat glands, it consists of glandular parenchyma (15-20 lobes with alveoli), ducts, and supportive stroma (fat and connective tissue).
Key Points To Remember
- Nipple: protrudes at the center, surrounded by pigmented areola containing sebaceous (Montgomery’s) glands for lubrication during lactation.
- Areola: darkens during pregnancy to aid newborn location.
- Lactiferous ducts: (one per lobe) drain milk from lobules, converge at nipple (15-20 openings).
- Ducts widen into lactiferous sinuses (ampullae) near nipple for milk storage.
- Mammary Alveolus: Alveoli cluster in lobules; myoepithelial cells contract to eject milk.
- Mammary Lobes: separated by fibrous septa (Cooper’s ligaments) extending to skin and pectoralis major.
- Fats: Fatty connective tissue fills bulk, determining breast size/shape; fibrous stroma anchors gland to chest wall.
Practice Questions
Q.6. In a longitudinal section of a human mammary gland, which labeled part directly opens on the surface of the nipple?
A. Lactiferous sinus
B. Lactiferous duct
C. Alveolus
D. Lobule
Q.7. Which labeled structure in a mammary gland diagram is the main site of milk synthesis and secretion?
A. Lactiferous sinus
B. Lobule connective tissue
C. Alveolus
D. Areola
Q.8. In a transverse section of the mammary gland, what does each lobule primarily contain?
A. Only adipose tissue
B. Blood vessels and nerves only
C. A group of alveoli and ducts
D. Only lactiferous sinuses
Q.9. Which part, usually labeled just beneath the areola, serves as a temporary storage chamber for milk?
A. Lactiferous sinus
B. Suspensory ligament
C. Alveolus
D. Secondary duct
Q.10. Which labeled part of the mammary gland diagram is responsible for ejecting milk from the alveoli into the duct system when stimulated by oxytocin?
A. Secretory epithelial cells
B. Adipocytes
C. Suspensory ligaments
D. Myoepithelial cells
Remember, mastering NEET diagrams isn’t about artistic perfection- it’s about speed, accuracy, and instant recall when the pressure is on. Keep revising, keep sketching, and most importantly, keep believing in your 650+ dream. See you tomorrow with another must-know diagram that brings you one confident step closer to your medical college seat!
Comment Below For Answers!
Sometimes we may miss a day or two in sharing the practice sets because of a few unavoidable commitments, but we truly appreciate your excitement and constant support for our content. Just like you are working hard to stay consistent with your NEET preparation, we are also putting in our best efforts to become more regular and better for you every single day.

