Most Important Biology Diagram For NEET UG 2026: Day 9 of our Most Important NEET UG Biology Diagrams series is here to make your preparation smarter, sharper, and a little more fun. Biology diagrams are not just drawings in your textbook; they’re powerful memory tools that can help you recall concepts instantly during the exam. Spend a few focused minutes today understanding this must-know diagram, and you’ll be one step closer to boosting your score toward your MBBS dream.
TROPHIC LEVEL
A trophic level is the position or step an organism occupies in a food chain or food web based on how it obtains its food or energy.
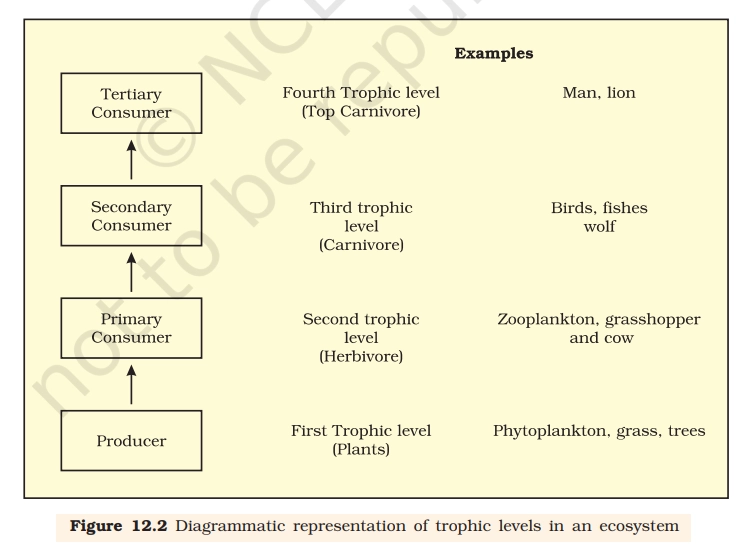
- Producer (1st trophic level)
- Plants, phytoplankton, grass, trees
- Prepare food by photosynthesis
- Base of the food chain and energy source for all higher levels
- Primary Consumer (2nd trophic level – Herbivores)
- Examples: zooplankton, grasshopper, cow
- Feed directly on producers
- Secondary Consumer (3rd trophic level – Carnivores)
- Examples: birds, fishes, wolf
- Feed on herbivores
- Tertiary Consumer (4th trophic level – Top carnivores)
- Examples: lion, man
- Occupy the highest trophic level in the food chain
Important NEET Concepts
- Energy flow is unidirectional: Sun → Producers → Consumers
- Energy decreases at each trophic level (10% law).
- Number of organisms decreases upward in the food chain.
- Top consumers are fewest but most energy-dependent.
- Humans can occupy multiple trophic levels (omnivores).
Read Also: NEET UG 2026 Daily Practice Questions To Score 650+ (DAY 23)
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Q.1. In a simple grassland food chain, which organism most appropriately represents a primary consumer at the second trophic level?
A. Hawk
B. Grass
C. Grasshopper
D. Frog
Q.2. Which statement best explains why energy decreases at each successive trophic level in an energy pyramid?
A. Energy is lost as heat and through life processes, so only a fraction is passed on.
B. Higher trophic levels are smaller, so they receive no energy from lower levels.
C. Energy is destroyed as organisms use it for movement and growth.
D. Most energy is converted into matter, so it disappears from the food chain.
Q.3. In an aquatic ecosystem, phytoplankton, zooplankton, small fish, and large fish form a food chain. Which organism occupies the third trophic level?
A. Phytoplankton
B. Zooplankton
C. Large fish
D. Small fish
Q.4. A forest ecosystem experiences a sharp decline in insect populations due to pesticide use. Which trophic level is most directly affected if many birds in this forest primarily feed on these insects?
A. Primary consumers
B. Producers
C. Tertiary consumers
D. Secondary consumers
Q.5. Why do top predators typically have smaller populations than organisms at lower trophic levels in the same ecosystem?
A. They receive less usable energy because of losses at each lower trophic level.
B. They reproduce more slowly, so they cannot maintain large populations.
C. They are less well adapted to their environment than prey species.
D. They are rarely part of food webs, so they lack access to consistent food sources.
Read Also: Most Important Biology Diagram For NEET UG 2026 (Day 8)
Structure of Anther
Anther is the terminal, fertile part of the stamen in a flower that produces and contains pollen grains inside structures called microsporangia (pollen sacs).
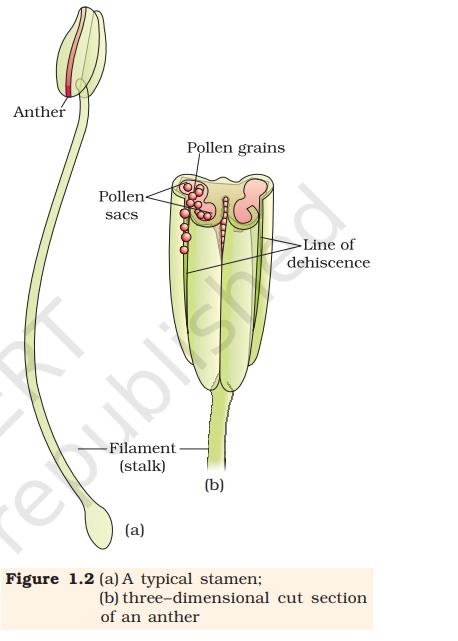
- Bilobed structure – A typical angiosperm anther has two lobes.
- Dithecous condition – Each lobe contains two theca, making a total of four microsporangia (pollen sacs).
- Tetrasporangiate – Presence of four microsporangia is a key diagnostic feature.
Attachment & Parts
- Filament – Long slender stalk that attaches anther to the flower.
- Anther – Terminal fertile part where pollen grains are produced.
- Line of dehiscence – Region where the anther splits open to release pollen.
Microsporangium (Pollen Sac)
- Each microsporangium is surrounded by four wall layers:
- Epidermis – Protective outer layer
- Endothecium – Helps in anther dehiscence
- Middle layers – Temporary layers that degenerate later
- Tapetum – Nutritional layer for developing pollen grains (very important for NEET)
Pollen Formation
- Microsporangia contain sporogenous tissue.
- Sporogenous cells undergo meiosis → microspore tetrads → pollen grains.
Quick NEET Memory Tricks
- “Bi-Di-Tetra-Four” → Bilobed → Dithecous → Tetrasporangiate → Four wall layers.
- Tapetum = Nutrition + Enzymes → Essential for fertile pollen.
- Endothecium = Dehiscence mechanism.
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Q.1. In a typical dithecous anther diagram, how many microsporangia are present and how are they arranged?
A. Two microsporangia, both in a single lobe
B. Two microsporangia, one in each lobe
C. Four microsporangia, arranged in a single row across the anther
D. Four microsporangia, two in each lobe
Q.2. In a labelled transverse section of a young microsporangium, which tissue forms the outermost layer and what is its primary function?
A. Endothecium; absorbs water for pollen maturation
B. Middle layers; formation of pollen grains
C. Tapetum; provides mechanical strength
D. Epidermis; protection of internal tissues
Q.3. A diagram of a developing microsporangium shows densely packed, large, deeply staining cells in the centre of each microsporangium. What do these cells represent?
A. Middle layer cells
B. Endothecial cells
C. Sporogenous tissue (pollen mother cell precursors)
D. Epidermal cells
Q.4. In a labelled longitudinal section of a stamen, which part of the anther is directly attached to the filament, and how is this connection represented in diagrams?
A. Microsporangium; shown as a stalk entering each pollen sac
B. Connective; shown as a central tissue continuation from the filament into the anther
C. Endothecium; shown as thickened bands extending into the filament
D. Tapetum; shown as a ring of cells merging with the filament
Q.5. In a diagram of a mature pollen sac (microsporangium) just before dehiscence, which of the following features is most likely to be absent or highly reduced compared to a young microsporangium?
A. Epidermis
B. Tapetum
C. Endothecium with fibrous thickenings
D. Microspores (pollen grains)
Read Also: Best NEET UG 2026 Timetable to Score 650+
Great job completing Day 9! Consistent daily practice like this builds strong conceptual clarity and confidence for the big day. Keep revising, keep drawing, and most importantly, keep believing in your journey to becoming a doctor.
Drop A Comment For Answers!

