NEET Important Biology Diagram 2026: Preparing for NEET UG 2026 requires smart revision strategies, and one of the most effective ways to strengthen Biology concepts is by mastering important diagrams.
In today’s NEET Important Biology Diagram 2026 (Day 11), we bring you a carefully selected diagram that frequently appears in exams and helps you revise key structures, labels, and functions in a quick and visual way. Regular practice of such diagrams not only improves retention but also boosts confidence for scoring higher in the Biology section.
MONOCOT & DICOT ROOT
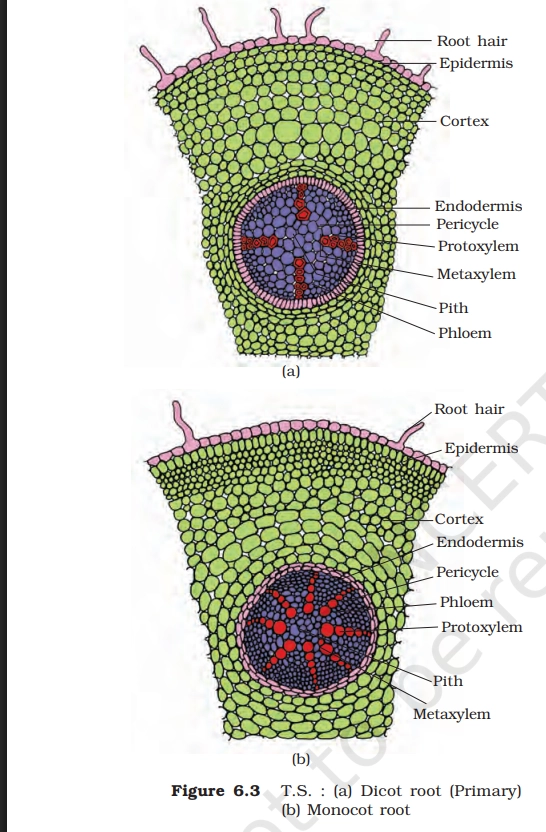
Key Points To Remember
1. Root Hair
- Absorbs water and dissolved minerals from the soil
- Increases surface area for absorption
2. Epidermis (Epiblema)
- Protects the root
- Helps in absorption of water and minerals
- Bears root hairs
3. Cortex
- Stores food (mainly starch)
- Helps in conduction of water from epidermis to vascular tissues
- Provides mechanical support
4. Endodermis
- Regulates entry of water into the stele (due to Casparian strips)
- Acts as a selective barrier
- Maintains internal root pressure
5. Pericycle
- Gives rise to lateral roots
- Contributes to secondary growth (vascular cambium formation in dicots)
- Provides limited support
6. Protoxylem
- First-formed xylem
- Conducts water and minerals during early growth
- Located towards the periphery of xylem
7. Metaxylem
- Later-formed xylem
- Conducts larger amounts of water
- Located more centrally than protoxylem
8. Phloem
- Transports food (sugars) from leaves to root and other parts
- Supports metabolic activities of root cells
9. Pith
- Storage of food (more prominent in monocot roots)
- Provides internal support
10. Conjunctive Tissue
- Parenchymatous tissue between xylem and phloem
- Helps in storage and later forms cambium in dicots
Read Also: NEET UG 2026 Daily Practice Set To Score 650+ (DAY 26)
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Q.1. In a typical T.S. of a dicot seed like pea, which feature best indicates that the seed is dicotyledonous rather than monocotyledonous?
A. A single, large shield-shaped cotyledon attached to the embryonic axis
B. Two large, fleshy cotyledons that almost completely fill the seed cavity
C. Endosperm occupying most of the space with a small embryo at one side
D. Presence of scutellum, coleoptile and coleorhiza around the embryo
Q.2. When comparing T.S. of monocot and dicot seeds, which statement correctly describes the typical position and relative size of the endosperm?
A. In dicots, the endosperm is more extensive than in monocots and forms the main storage tissue
B. In both monocots and dicots, endosperm always remains the main storage tissue in the mature seed
C. In monocots, the endosperm is extensive and surrounds the embryo; in many dicots it is reduced or absent
D. In both, the endosperm is completely absent in the mature seed
Q.3. In a T.S. of a dicot seed, what is the typical location of the embryonic axis relative to the two cotyledons?
A. Surrounded by endosperm and not attached to cotyledons
B. Positioned entirely outside the cotyledons near the seed coat
C. Lying between the two cotyledons, connecting them at one side
D. Completely embedded within a single cotyledon
Comment Below for Answers!
We understand that revising everything at once might be a heavy task for you all, but let us know if we can help you in any way. As our team is dedicatedly working on NEET strategies, practice papers, and PYQ analysis to bring the best resources.
Your feedback and comments inspire us to work hard and do our best. We also request that you share our content with your fellow aspirants, so that they do not need to roam here and there for NEET Resources.
ALL THE VERY BEST!
Read Also: How To Access NEET UG 2026 Daily Quizzes & Diagrams on Edufever

