Daily Practice MCQ For NEET UG 2026: Consistency is the real game-changer in competitive exams like NEET UG, and nothing builds consistency better than daily practice questions. Solving a fixed set of well-designed MCQs every day not only strengthens your grip on NCERT concepts but also trains your brain to think under exam-like pressure. Daily practice helps you identify weak areas early, improve accuracy, and develop the speed required to convert knowledge into marks. Whether you are aiming for a safe score or a top rank, disciplined daily practice is the bridge between preparation and performance.
PHYSICS
Q.1. A thin spherical shell is charged by some source. The potential difference between the two points C (in C) and P (in V) shown in the figure is:
(Take 4πε01=9×109 SI units)
Radius, R=3cm
Charge on shell, q=1μC
Options:
(1) 3×105
(2) 1×105
(3) 0.5×105
(4) Zero
READ ALSO: Daily Practice MCQ For NEET UG 2026 to score 650+ (DAY 5)
Q.2. The output (Y) of the given logic gate is similar to the output of an/a:
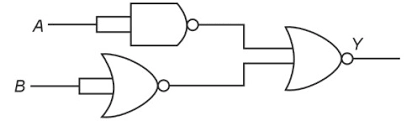
(1) NAND gate
(2) NOR gate
(3) OR gate
(4) AND gate
Q.3. If the monochromatic source in Young’s double slit experiment is replaced by white light, then
(1) Interference pattern will disappear
(2) There will be a central dark fringe surrounded by a few coloured fringes
(3) There will be a central bright white fringe surrounded by a few coloured fringes
(4) All bright fringes will be of equal width
Q.4. In a vernier calipers, (N+1) divisions of vernier scale coincide with N divisions of main scale.
If 1 MSD represents 0.1 mm, the vernier constant (in cm) is:
(1) 10N1
(2) 100(N+1)1
(3) 100N
(4) 10(N+1)
Q.5. The maximum elongation of a steel wire of 1 m length if the elastic limit of steel and its Young’s modulus, respectively, are
8×108N m-2 and 2×1011N m-2, is:
(1) 4 mm
(2) 0.4 mm
(3) 40 mm
(4) 8 mm
CHEMISTRY
Q.6. Identify the correct reagents that would bring about the following transformation:
Cyclohexyl-CH₂-CH=CH₂ ⟶ Cyclohexyl-CH₂-CH₂-CHO
Options:
(1)
(i) H₂O / H⁺
(ii) CrO₃
(2)
(i) BH₃
(ii) H₂O₂ / OH⁻
(iii) PCC
(3)
(i) BH₃
(ii) H₂O₂ / OH⁻
(iii) alkaline KMnO₄
(iv) H₃O⁺
(4)
(i) H₂O / H⁺
(ii) PCC
Q.7. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is present in:
(1) o-Nitrophenol
(2) p-Nitrophenol
(3) m-Nitrophenol
(4) HF
Q.8. Activation energy of any chemical reaction can be calculated if one knows the value of:
(1) Rate constant at standard temperature
(2) Probability of collision
(3) Orientation of reactant molecules during collision
(4) Rate constant at two different temperatures
Q.9. Match List I with List II.
List I (Complex):
A. [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl2
B. [Co(NH3)5(SO4)]Br
C. [Co(NH3)6][Cr(CN)6]
D. [Co(H2O)6]Cl3
List II (Type of isomerism):
I. Solvate isomerism
II. Linkage isomerism
III. Ionization isomerism
IV. Coordination isomerism
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(1) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(2) A-I, B-III, C-IV, D-II
(3) A-I, B-IV, C-III, D-II
(4) A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I
Q.10. 1 gram of sodium hydroxide was treated with 25 mL of 0.75 M HCl solution.
The mass of sodium hydroxide left unreacted is equal to:
(1) 750 mg
(2) 250 mg
(3) Zero mg
(4) 200 mg
BIOLOGY
Q.11. Which of the following is an example of actinomorphic flower?
(1) Datura
(2) Cassia
(3) Pisum
(4) Sesbania
Q.12. Identify the set of correct statements:
A. The flowers of Vallisneria are colourful and produce nectar.
B. The flowers of water lily are not pollinated by water.
C. In most of water-pollinated species, the pollen grains are protected from wetting.
D. Pollen grains of some hydrophytes are long and ribbon-like.
E. In some hydrophytes, the pollen grains are carried passively inside water.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(1) C, D and E only
(2) A, B, C and D only
(3) A, C, D and E only
(4) B, C, D and E only
Q.13. A pink flowered Snapdragon plant was crossed with a red flowered Snapdragon plant. What type of phenotype/s is/are expected in the progeny?
(1) Only red flowered plants
(2) Red flowered as well as pink flowered plants
(3) Only pink flowered plants
(4) Red, pink as well as white flowered plants
Q.14. Formation of interfascicular cambium from fully developed parenchyma cells is an example of:
(1) Differentiation
(2) Redifferentiation
(3) Dedifferentiation
(4) Maturation
Q.15. Match List I with List II
List I
A. Two or more alternative forms of a gene
B. Cross of F₁ progeny with homozygous recessive parent
C. Cross of F₁ progeny with any of the parents
D. Number of chromosome sets in plant
List II
I. Back cross
II. Ploidy
III. Allele
IV. Test cross
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(1) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(2) A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
(3) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(4) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
Remember, success in NEET is not achieved by studying occasionally for long hours, but by showing up every day and solving questions with focus. Stay consistent, trust the process, and keep improving one day at a time. Small daily efforts, when compounded over months, lead to extraordinary results in the exam hall.
READ ALSO: Daily Practice MCQ For NEET UG 2026 to score 650+ (DAY 4)
ANSWERS & EXPLANATIONS:
Answer 1: (4) Zero
Explanation:
- Potential inside a charged spherical shell is constant and equal to surface potential.
- Points C (inside) and P (on surface) — same potential
- ∴ Potential difference = 0
Answer 2: (4) AND gate
Explanation:
- Given circuit first inverts inputs A and B
- Final gate is NOR — Output = (A̅ + B̅)̅ = A·B
- Equivalent to AND gate
Answer 3: (3) Central bright white fringe surrounded by coloured fringes
Explanation:
- At zero path difference — all wavelengths constructively interfere — white fringe
- Away from centre — colours separate
Answer 4: (2)
Explanation:
- VC = 1 MSD – 1 VSD
- Given: (N+1) VSD = N MSD
- VC = N(N+1)1 MSD
- 1 MSD = 0.1 mm = 0.01 cm
Answer 5: (2) 0.4 mm
Explanation:Strain=YStress=2×10118×108=4×10−3ΔL=L×strain=1×4×10−3=0.004m=0.4mm
Answer 6: (2)
Explanation:
- Hydroboration–oxidation — anti-Markovnikov alcohol
- PCC oxidizes alcohol — aldehyde
Answer 7: (1) o-Nitrophenol
Explanation:
- Ortho position allows internal H-bonding
Answer 8: (4)
Explanation:
- Arrhenius equation requires rate constants at two temperatures
Answer 9: (1)
Explanation:
- NO₂⁻ — linkage
- SO₄²⁻ — ionization
- Complex-complex salt — coordination
- Hydrated salt — solvate
Answer 10: (2) 250 mg
Explanation: The neutralization reaction between NaOH and HCl is:
NaOH+HCl→NaCl+H2O
Given:
- Mass of NaOH = 1 g
- Molar mass of NaOH = 40 g/mol
Moles of NaOH: Mass /Molar mass = 1/40=0.025 mol
Given:
- Volume of HCl = 25 mL = 0.025 L
- Molarity of HCl = 0.75 M
Moles of HCl:
Moles of HCl=M×V=0.75×0.025=0.01875 mol
The reaction follows a 1:1 molar ratio between NaOH and HCl.
- NaOH available: 0.025 mol
- HCl available: 0.01875 mol
Since HCl has fewer moles, it is the limiting reagent.
Unreacted moles of NaOH:
Unreacted NaOH=0.025-0.01875=0.00625 mol
Mass of unreacted NaOH:
Mass=0.00625×40=0.25 g=250 mg
Correct Answer 11: (1) Datura
Explanation:
- Actinomorphic — Radial symmetry (cut into two equal halves in any plane).
- Datura shows radial symmetry.
- Cassia, Pisum, Sesbania are zygomorphic.
Correct Answer 12: (4) B, C, D and E only
Explanation:
- A Vallisneria flowers are not colourful and do not produce nectar.
- B Water lily is pollinated by insects, not water.
- C Pollen grains are protected from wetting.
- D Some hydrophytes have ribbon-like pollen.
- E In some cases pollen is carried passively by water.
Correct Answer 13: (2) Red flowered as well as pink flowered plants
Explanation:
- Snapdragon shows incomplete dominance.
- Cross: Pink (Rr) × Red (RR)
- Progeny:
- 50% RR — Red
- 50% Rr — Pink
Correct Answer 14: (3) Dedifferentiation
Explanation:
- Dedifferentiation — Mature, differentiated cells regain the ability to divide.
- Parenchyma becoming cambium = dedifferentiation.
Correct Answer 15: (3) A–III, B–IV, C–I, D–II
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Allele | Alternative forms of a gene |
| Test cross | F₁ × homozygous recessive |
| Back cross | F₁ × any parent |
| Ploidy | Number of chromosome sets |
GOOD LUCK!!
Drop Your Scores In Comments!!



Mam question no 2 and 10 feels something incomplete 😌 missing something in explanation
Thanks for highlighting. Kindly check again.
Better level questions covering all major portions thankyou mam 12/15📈