Most Important Biology Diagram For NEET UG 2026: Welcome to Day 5 of our Most Important Biology Diagrams series, your daily dose of high-yield visual learning straight from NCERT. Diagrams in Biology are not just pictures; they are quick memory tools that help you recall complex concepts in seconds during the exam. Today’s diagram is carefully chosen to strengthen your fundamentals, boost accuracy, and make revision smarter and faster. So keep your notes ready and let’s decode another must-know NEET diagram together!
PLANT CELL
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells found in plants, distinguished by a rigid cell wall, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and a large central vacuole. These features enable plants to produce food from sunlight, maintain structure without a skeleton, and store nutrients.
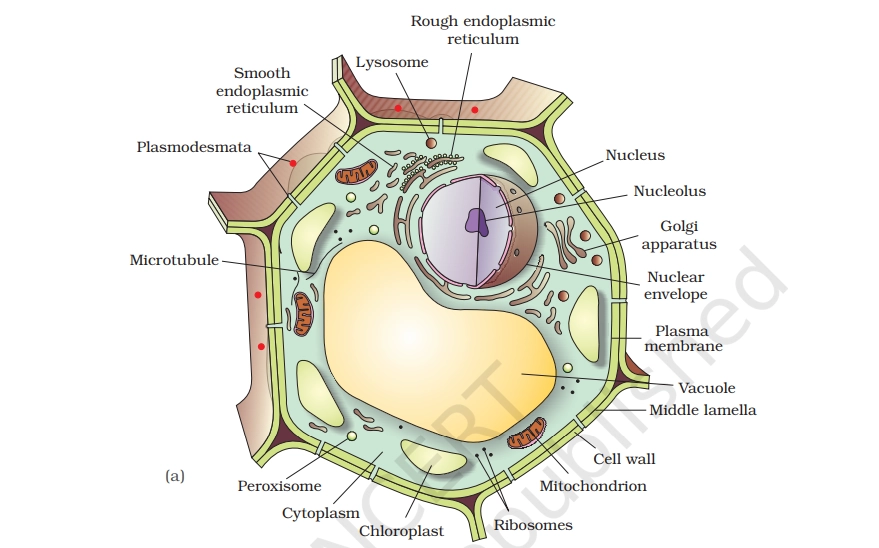
Key Points To Remember
- Cell Wall: Rigid outer layer of cellulose providing structural support, protection from mechanical stress, and filtering molecules.
- Plasma Membrane: Semi-permeable barrier inside the cell wall controlling entry/exit of substances like water and nutrients.
- Nucleus: Contains DNA, nucleolus, and controls cell activities including growth and reproduction.
- Cytoplasm: Jelly-like fluid housing organelles, enabling chemical reactions and molecule transport.
- Central Vacuole: Large storage sac (up to 90% of cell volume) maintaining turgor pressure, storing water/nutrients, and waste disposal
- Chloroplasts: Green organelles with chlorophyll for photosynthesis, converting light into glucose energy.
- Mitochondria: Powerhouses producing ATP energy via cellular respiration.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Rough ER (with ribosomes) synthesizes proteins; smooth ER makes lipids and detoxifies.
- Golgi Apparatus: Stacks modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins/lipids for secretion or use.
- Ribosomes: Protein synthesis sites, free in cytoplasm or on rough ER.
- Plasmodesmata: Channels connecting adjacent cells for nutrient/hormone exchange.
Read Also: Most Important Biology Diagram For NEET UG 2026 (Day 4)
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Q.1. On a typical plant cell diagram, which labeled structure is primarily responsible for maintaining turgor pressure and storing water, pigments, and some wastes?
A. Nucleus
B. Golgi apparatus
C. Chloroplast
D. Central vacuole
Q.2. A diagram shows a thick outer layer surrounding the plant cell membrane. Which labeled structure provides this rigid support and is mainly made of cellulose?
A. Plasma membrane
B. Middle lamella
C. Cell wall
D. Cytoskeleton
Q.3. On a labeled plant cell diagram, which structure should be identified as the main site of photosynthesis, containing the pigment that captures light energy?
A. Chloroplast
B. Mitochondrion
C. Peroxisome
D. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Q.4. A student labels a large, oval structure near the center of the plant cell diagram as the “control center” of the cell. Which organelle is being labeled, and what is its main function?
A. Ribosome; it forms the rigid outer covering of the cell
B. Nucleolus; it stores water and maintains turgor pressure
C. Nucleus; it stores genetic information and coordinates cell activities
D. Chloroplast; it packages proteins for secretion
Q.5. On a plant cell diagram, which labeled boundary correctly represents the selective barrier that controls the movement of substances into and out of the cytoplasm, just inside the cell wall?
A. Middle lamella
B. Secondary cell wall
C. Plasma membrane
D. Nuclear envelope
ANIMAL CELL
An animal cell is the basic structural and functional unit of animal tissues, a eukaryotic cell enclosed by a plasma membrane without a rigid cell wall, enabling flexibility and diverse shapes.
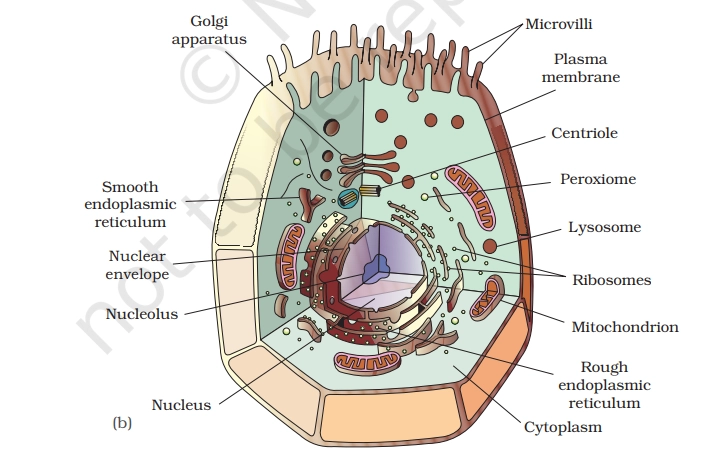
Key Points To Remember
- Plasma Membrane: Selective barrier controlling entry/exit of substances, maintaining cell integrity.
- Nucleus: Control center housing DNA and nucleolus, directing cell growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
- Cytoplasm: Fluid matrix suspending organelles, site of metabolic reactions and transport.
- Mitochondria: Powerhouses generating ATP via cellular respiration for energy needs.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Rough ER (with ribosomes) synthesizes proteins; smooth ER produces lipids and detoxifies.
- Golgi Apparatus: Modifies, packages, and ships proteins/lipids for secretion or internal use.
- Ribosomes: Sites of protein synthesis, free-floating or attached to rough ER.
- Lysosomes: Digestive sacs breaking down waste, pathogens, and old organelles.
- Centrioles: Organize spindle fibers during cell division (absent in plant cells).
- Cytoskeleton: Network of microfilaments and microtubules for shape, support, and movement.
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Q.6. In a typical animal cell diagram, which labeled structure is most directly responsible for producing ATP during cellular respiration?
A. Mitochondrion
B. Nucleus
C. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
D. Golgi apparatus
Q.7. On an animal cell diagram, a student labels a network of membranes studded with ribosomes near the nucleus. Which main function best matches this labeled structure?
A. Detoxification of drugs and poisons
B. Breakdown of worn-out organelles using enzymes
C. Synthesis and initial folding of proteins for secretion or membranes
D. Storage of genetic information
Q.8. In a labeled animal cell diagram, which structure forms a selective barrier that controls what enters and leaves the cell?
A. Cytoskeleton
B. Cell (plasma) membrane
C. Nuclear envelope
D. Cell wall
Q.9. A diagram shows small, membrane-bound sacs pinching off from the Golgi apparatus and moving toward the cell membrane. What is the main role of these labeled structures?
A. Producing ATP for cellular activities
B. Carrying proteins and lipids for secretion outside the cell
C. Storing genetic information
D. Digesting old organelles
Q.10. In an animal cell diagram, which labeled structure contains digestive enzymes and is responsible for breaking down worn-out cell parts and macromolecules?
A. Peroxisome
B. Lysosome
C. Centrioles
D. Ribosome
Read Here: Daily Practice Questions For NEET UG 2026 to score 650+ (DAY 19)
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
The male reproductive system consists of organs that produce, store, and deliver sperm for reproduction while secreting male sex hormones like testosterone.
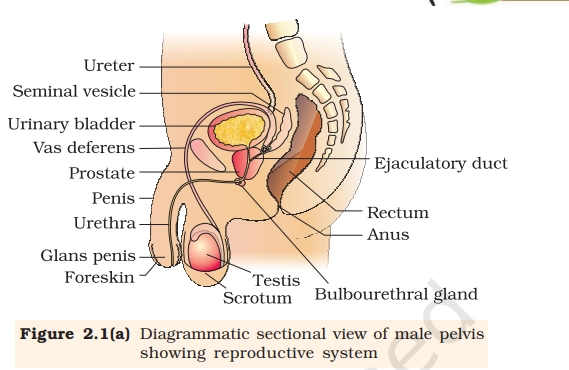
Key Points To Remember
- Testes (Testicles): Paired gonads in the scrotum producing sperm and testosterone to regulate male traits.
- Scrotum: External sac suspending testes, regulating temperature for optimal sperm production.
- Epididymis: Coiled tube atop each testis where sperm mature and gain motility.
- Vas Deferens: Muscular duct transporting mature sperm from epididymis to urethra.
- Seminal Vesicles: Glands secreting fluid rich in fructose to nourish and energize sperm.
- Prostate Gland: Surrounds urethra, adds alkaline fluid to semen neutralizing vaginal acidity.
- Bulbourethral Glands (Cowper’s): Secrete pre-ejaculatory fluid lubricating urethra.
- Penis: External organ for semen delivery during intercourse; contains urethra for urine/semen passage.
- Urethra: Tube through penis expelling semen or urine.
- Spermatic Cord: Supports vas deferens, blood vessels, and nerves to testes.
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Q.11. On a diagram of the male reproductive system, which structure is correctly labeled as the site where sperm are stored and mature after leaving the testis?
A. Vas (ductus) deferens
B. Prostatic urethra
C. Seminiferous tubules
D. Epididymis
Q.12. On a labeled diagram, which structure should be identified as the primary site of testosterone production in the male?
A. Epididymis
B. Interstitial (Leydig) cells in the testes
C. Bulbourethral (Cowper’s) glands
D. Seminal vesicles
Q.13. Which structure, usually seen running from the scrotum into the pelvic cavity on a diagram, is correctly labeled as the tube that transports sperm from the epididymis toward the urethra during ejaculation?
A. Penile urethra
B. Rete testis
C. Vas (ductus) deferens
D. Ejaculatory duct
Q.14. When labeling a frontal section of the male pelvis, which structure should be identified as producing a fructose-rich, alkaline fluid that constitutes a large portion of semen volume?
A. Bulbourethral glands
B. Seminal vesicles
C. Prostate gland
D. Epididymis
Q.15. A diagram shows a cross-section through the scrotum with an arrow pointing to the sac that encloses each testis and helps regulate testicular temperature. Which structure should that arrow label?
A. Spermatic cord
B. Dartos muscle
C. Tunica vaginalis
D. Tunica albuginea
COMMENT BELOW FOR ANSWERS!
Dear Students, The answers are shared a day later on purpose. When you come back the next day to check your comment, you end up looking at the diagrams once again, giving you a quick and easy revision without extra effort. This simple habit helps you remember concepts better, improves retention, and keeps important topics fresh for your NEET preparation.

